You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Policy’ category.
Over 10 years, Xi Jinping has methodically amassed power. Beginning with an unprecedented consolidation of military support, Xi then launched his ‘Tigers and Flies’ campaign, sidelining his political rivals along with officials accused of corruption. Over many years he patiently laid the groundwork to elevate Xi Jinping Thought to match the official stature of Mao Zedong Thought, and edge out Deng Xiaoping Thought, in the CCP’s ideological pantheon. He then overturned international commitments regarding Hong Kong, and brought that free-wheeling and Westernized city to heel with the introduction of a new security law. At the last 19th Party Congress in 2017, Xi tossed aside Deng’s “hide-and-abide” (韜光養晦、有所作為) approach to international relations and gave a triumphalist speech, announcing that China had not only arrived on the world stage but that it deserved central position on that stage. With the outbreak of the Covid-19 epidemic, Xi used sharp-elbow tactics to block scientific investigation into its origins in China and ordered sweeping zero-Covid lockdowns to highlight his government’s ability to take more effective action than was possible for democratic governments in the US and the West. The Winter Olympics were meant to be Xi’s star-turn to demonstrate — more to the Chinese people than to international audiences (many of whom undertook diplomatic boycotts of the Games because of oppression of Uyghurs in Xinjiang and other issues) — that he was a flawless and unrivalled champion. He even went so far as to claim that the authoritarian system he presided over represented a superior form of democracy to Western liberal democracy.

Along this path to unrivalled power in China, Xi first jettisoned the system of collective rule by the Standing Committee of the Politburo which Deng had put in place to guard against recurrence of unbridled rule by any one individual, epitomized by the last years of Mao’s rule. Longer term, Xi’s aim in amassing power has been to discard the limit of a president to two five-year terms, another safeguard Deng put in place and which he himself observed.
The announcement of leadership for the next five-year term will happen at the CCP’s 20th Party Congress in Beijing this autumn. At that meeting, Xi is widely expected to be named for a precedent-shattering third term. This will mark a historic high-point for Xi. His systematic consolidation of power has been designed, in part, to create an air of inevitability about this outcome. While his selection is still overwhelmingly likely, a number of significant fissures have appeared in recent weeks which crack this façade of total control.
ZERO-COVID
While undoubtedly successful in limiting the number of infections, hospitalizations, and deaths in the first two years of the pandemic, Xi’s Zero-Covid policy has created a raft of problems for China more recently, most notably during the highly-transmissible omicron phase. While incidences of infection, hospitalization and death have been dropping worldwide, they have been surging in China, with the number of confirmed cases more than quadrupling from mid-February to mid-March of this year. Elderly citizens are especially at risk due to their low rates of vaccination and hospitals have already become overwhelmed, due in part to the low number of hospital beds on a per capita basis in China. While it can be argued that the Zero-Covid policy ‘bought time’ for the development of vaccines, Xi’s championing of the locally developed Sinovac vaccine and his refusal to permit the use of more clinically-effective vaccines developed in the West, has blunted that advantage somewhat since the Sinovac vaccine is notably less effective against the omicron variant. The Zero-Covid policy has also meant that there is practically zero immunity in the Chinese population as a result of exposure to the virus as it becomes endemic worldwide. If SARS-COV-2 can be compared to a flame, China’s population is like a vast field of tinder. Finally, the economic and social costs have become glaringly apparent with the lockdown of an entire province, Jilin, in the northeast and the of Shenzhen and Dongguan – China’s two largest manufacturing hubs for information and communications technology (ICT) — in the south.
While Xi will, with considerable justification, continue to claim credit for his “triumph” over the coronavirus, China is by no means out of the pandemic woods and the setbacks of the last month make his strident claims ring more hollow, both internationally and domestically.
REAL ESTATE
In September last year, Chinese real-estate development firms began to feel the severe discomfort of a massive hang-over following years of real-estate speculation partying. The problems were most evident in real-estate giant Evergrande but soon spread to a host of other significant players in the field such as Fantasia, Modern Land, China Property Group and Xinyuan Real Estate Group. At the institutional level, the problems hitting the $5 trillion sector were the result of a unique PRC nexus of aggressive real estate development, lax banking, and local government incentive structures. More simply, the problems resulted from “unrestrained borrowing, expansion as an end-in-itself, and corruption.”
While the PRC Government claimed this week that the real-estate free-fall has been “stabilized,” pricing data from real estate developers across the country continue to show sharp deterioration. Also this week, Evergrande announced a further delay in sharing its plan for restructuring and for paying back bonds and other financial obligations. The government has strong reason to put on a brave face while throwing up a curtain of opacity around the problem. Property-related industries account for more than 30% of China’s economic output. Continued problems in the sector could drag China’s growth below the optimistic, post-pandemic official target of 5% growth, a minimum level which must be maintained in the years ahead for China to escape the ‘middle income trap.’ More immediately, it risks alienating an important swath of the urban public, 80% of whose household wealth is tied up in real estate and who see their property values plummeting. (A particularly aggrieved segment of this population are buyers who have paid up front to the developers, as is common in China, for a property not yet built and for which construction has halted indefinitely while values continue to slide).
While Xi has voiced loud promises to not let the bottom fall out of this sector and to support homeowners currently caught in the fallout, there is little evidence on the ground of these promises translating into reality. Meanwhile, the situation risks alienating the public and sowing dissent among officials.
‘COMMON PROSPERITY’
As measured by the Gini coefficient, China ranked fourth in the world in 2022 for greatest wealth disparity and inequality (after South Africa, Namibia and Sri Lanka). While Deng Xiaoping had announced famously in the late 1980s that “to get rich is glorious” and to “let some get rich first,” the extreme degree of inequality persisting in China four decades later is a source of growing social and political concern. The heady days of 10% growth have long ago disappeared and Chinese who thought they would be boarding on a later rail-car in the national train of prosperity now worry that the train may have departed, stranding them on the platform.
To counter this source of social unease, Xi unveiled with great fanfare in 2021 a policy of ‘Common Prosperity.” Writ large, this policy was meant to cement Xi’s place — side-by-side with Mao and with Deng slightly in the background – in China’s pantheon of modern heroes. In this telling, Mao was the one who roused China to throw off its ‘Sick Man of Asia’ bondage to foreign imperialists and to stand up. Deng contrived a transitional stage of capitalist-style wealth-creation for enough Chinese that China could attain wealth and power (富权). It was left to Xi to complete this project of national rejuvenation, by reinstituting a Marxist “Common Prosperity’ for all Chinese and returning China to the center of the world stage.
Without getting into either the ideological weeds (such as Xi’s ‘Dual Circulation’ strategy) or deep into the tangle of economic measures (e.g., restrictions on overseas listings by Chinese companies, user-data and other controls put on Chinese Big Tech firms, clampdown on student test-prep and video game commercial sectors, etc) which Xi embraced in 2021 to advance his Common Prosperity agenda, the general effect was felt quickly and keenly in the form of abrupt economic slowdown. In the first quarter of this year, the Common Prosperity program has been ‘walked back’ by numerous party officials who have emphasized that it represents a historic project more than an immediate project. Premier Li Keqiang, in his lengthy speech to 3,000 deputies at the opening of the National People’s Congress earlier in the month, mentioned Common Prosperity only one time. For educated Chinese — who have been skillfully parsing official pronouncements closely ever since the Cultural Revolution for clues about where the country is headed — this lack of visibility and endorsement for Xi Jinping’s signature program represents a remarkable degree of push-back for Xi by top-level leaders.
UKRAINE
Chris Buckley’s report in last Friday’s New York Times traces the contours of what is potentially the most damaging crack to appear in Xi’s carefully-crafted, monolithic façade of power and control. The article details the war of words that has erupted on the Chinese internet following the warning delivered by a respected scholar and politically-connected insider, Hu Wei, to the effect that China “risked becoming a pariah if it didn’t denounce Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.” As was covered in last week’s post and as continues to play out this week, Chinese officials have contorted themselves by claiming to be neutral and wanting peace while following Putin’s lead in not calling the ‘special military operation’ either a war or an invasion, in not objecting to Russia’s violation of Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, and in amplifying Kremlin disinformation about U.S. bio-military labs in Ukraine.
As argued last week, this has the potential to grow into a strategic blunder for China with significant geopolitical fall-out. It may affect not only Xi’s ambitions to retake Taiwan – the last territorial piece in his China Rejuvenation plan – but to bear long term costs for China as a rising power in the Indo-Pacific region and for its standing in the world at large.
None of this is to suggest that Xi will not get his third term as President this fall. It is only to say that the carefully-cultivated blooms of infallibility and inevitability are now off the XJP rose.
Xi has been in power for less than half of Putin’s tenure (18 years as President and 4 years as the power behind the throne for Medvedev) but there are doubtless people in Zhongnanhai wondering to themselves, post-Putin’s invasion, whether Deng didn’t get it right with his moves to limit the untrammeled exercise of power by an individual leader.
On February 4th, at the conclusion of their day-long summit in Beijing, Vladimir Putin and Xi Jinping declared that the friendship between Russia and China “has no limits.” That same day, the Beijing Winter Olympics officially began, ending a little more than two weeks later on February 20th. On February 24th, Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine began.
There has been extensive analysis of the three major miscalculations Putin has made up to this point: (1) his overestimation of the readiness and effectiveness of his military machine; (2) his underestimation of the resilience and fighting spirit of the Ukrainian people; and (3) the speed and scale with which NATO and EU countries, along with many others, have come together to sanction Russia and to support Ukraine (in all ways short of direct military involvement on, or in the air above, Ukrainian territory). It is too early to tell whether a fourth major miscalculation may have to do with Putin’s misplaced faith in the degree of economic, financial and trade support which China would provide Russia to backfill against these sanctions).
But what about Xi Jinping? What is his calculus for advancing (his interpretation of) China’s interests through this crisis? And what miscalculations has he appeared to have made so far?
Xi’s first miscalculation was immediate and damaging. He is known to have had some discussion with Putin on Feb. 4th about the imminent “special operation” in Ukraine. It is not clear whether Putin lied to him or Xi simply failed to ask the right questions to take Putin’s measure. In either case, Xi Jinping is known to have been caught by surprise and ‘perturbed’ by the scale, duration and ruthlessness of Putin’s “special operation.” As described in my February 4th post “Four Seismic U.S.-China-Russia Shifts,” Putin’s move forced Xi, unexpectedly and very publicly, to choose between his new-found friendship without limits and adherence to China’s mantra-like stated policy of non-interference in the affairs of sovereign nations, as enunciated in 1954 in Zhou Enlai’s Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence (and championed explicitly with regard to Ukraine’s territorial integrity following Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014)
Evidence of Xi’s miscalculation of Putin’s intentions in Ukraine became apparent in the initially hesitant and fence-sitting response by the PRC officials during the first two weeks of the crisis. On the one hand, Chinese officials refused to refer to the invasion publicly with any term other than Putin’s Orwellian “special operation” terminology; pivoted reliably to blaming the crisis on NATO rather than Russia aggression; blocked a series of actions from being taken against Russia in the U.N. Security Council; amplified Russian disinformation about the U.S. operating bio-military labs in Ukraine (a play out of the FSK, formerly KGB, playbook which suggests that Putin is contemplating the use of bio- or chemical weapons and is ready to throw sand in the world’s eyes by blaming the U.S. and/or NATO for their eventual use); and has even embedded Chinese journalists with Russian military units on the ground in Ukraine. On the other, China says its the friend of both Ukraine and Russia; talks about the need for the cessation of violence; offers publicly to mediate between the two sides while not actually taking any steps toward a mediation effort); and repeats the mantra of its Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence as if Putin’s actions in Ukraine were taking place in some parallel universe.
There have been other related miscalculatiions. For instance, the PRC Government has been repeatedly caught off balance by the Biden Administration’s aggressive use of classified U.S. intelligence findings, with his Administration quickly de-classifying key reports and pushing the information out into the public sphere, both domestically and internationally. This began with President Biden’s sharing in real-time with the world the U.S. intelligence community’s pre-invasion assessments that Putin had made the decision to invade. This very public use of previously hush-hush intelligence findings marks a clear break from past White House precedent and has also been aimed at China in recent weeks: first, in divulging the fact that Xi Jinping had prior knowledge of the invasion from his Feb. 4th meeting with Putin and that Xi had, in fact, asked Putin to hold off on initiating that military operation until after the conclusion of the Beijing Winter Olympics; and, second, in disclosing publicly on the eve of Secretary of State Anthony Blinken’s March 14th meeting with China’s top diplomat Yang Jiechi the fact that Beijing had received requests from Moscow for military and economic assistance to aid its war effort. These and other revelations have punctured China’s contrived public posture and shown that, behind the peaceful resolution rhetoric and thin veil of neutrality in the conflict, the reality is that China is not sitting on the fence but has indeed been coming down on Russia’s side.
The initial confusion in China’s response and now the growing evidence of China’s support, up to a point, for Russia were probably to be expected : under-the-table support for Putin was inevitable given the top-down nature of Chinese government decision-making and the personal investment which Xi had made in Putin and Russia just weeks earlier. Just as powerfully through, China wants to keep some fig-leaf semblance of its Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence policy because its repudiation would roil China’s international relations, among others, with its Belt & Road Initiative partner countries. Equally, it does not want to run afoul of the trip wire of U.S.-led financial and economic sanctions by aiding Russia overtly with military aid, financial relief or with trade in sanctioned commodities like microchips, especially following the stern warning delivered by Secretary Blinken earlier this week.
Over the last week, there are signs that the Beijing leadership is trying to “elevate” its initial indecision and aloofness into what it believes can be a long-term winning strategy for coming out ahead of the West when flames die out and the dust settles from the Ukraine conflagration. The Zhongnanhai thesis is that it is not worldwide supporters of post-WWII liberal democracy that are rallying to support Ukraine as much as it is a “civilizational” struggle between a Russian identity promulgated by Putin and a Western identity and set of values represented primarily by the U.S. and Europe. The thinking goes that, if China stands back from this clash, it can pick up the pieces and emerge stronger than either of the two depleted civilizational antagonists. This accords with Xi Jinping’s decade-long championing of the rejuvenation, and even superiority, of Han identity and the Chinese model. In Xi’s thinking, this policy of studious and disciplined aloofness — limited to cheering on Russia with “dog-whistle” encouragement and forms of back-channel support it can get away with while seizing opportunities to denigrate the West to his domestic audience and to countries in Central Asia, the Pacific, and Africa — has two clear advantages: (1) it avoids any risk for Xi in decisively backing ‘a loser’ in Putin, an outcome already sealed in his international pariah status and increasingly likely on the battlefield even if Kiev is taken and the war shifts to an insurgency; and (2) it gives Xi space to attend to the many immediate challenges facing him in the run-up to the critical Party Congress this fall where he is bidding for a third, controversial term as President. Those challenges include: a sharp fall-off in economic performance (brought on in part by excesses of his own Common Prosperity policy introduced over the past year; rapidly rising Covid case-counts and lock-downs in Shenzhen and Donguan in the south, in Shanghai and in Jilin to the northeast; and the recent hardening of attitudes toward China throughout much of the world as ably analyzed by Elizabeth Economy in The World According to China and in her Jan/Feb 2022 article in Foreign Affairs.
The jury is out but I submit that this policy of official aloofness may well prove to be Xi Jinping’s biggest and longest-lasting miscalculation with regard to Ukraine. Xi may think in ethno-nationalist terms, but much of the world’s response is underpinned by non-Western allies such as Japan, South Korea and Singapore who have benefitted from, and are committed to upholding, the post-WWII order based on national sovereignity and the rule of law. In fact, it is Taiwan which represents and symbolizes the fullest repudiation of Xi’s thesis. Absent some mis-adventure by North Korea (which is a disturbing possibility) or a premature move by Xi to extinguish the symbol Taiwan represents (which I consider very unlikely in the near-term), Xi’s official ‘aloofness’ and sub-rosa support for Putin will be remembered by the world in the wake of the Ukraine conflict. There are times when a person, or a nation, must choose sides. Not choosing sides in such situations is, in fact, a choice that is noticed and remembered. Pretending not to choose sides while actually backing the ‘wrong side’ is morally repugnant. There is not a middle way.

After a puzzling on-again, off-again trade action against China’s information and communications technology (ICT) giant ZTE in 2018, the Trump Administration began sanctioning China’s number #1 ICT player Huawei in May 2019. The sanctioning action involved putting Huawei on a Commerce Department “entity list” and thereby restricting U.S. suppliers from selling their goods and technology to Huawei.
As with all of Trump’s trade actions against China, impulse outweighed well thought-out execution in the Huawei crackdown. Initially, some sales were allowed and others denied without clear criteria being communicated to U.S. industry. Later, without preparatory signaling, the Huawei campaign was intensified by expanding U.S. government authority to require licenses for sales of semiconductors made abroad with American technology.
The fitfulness of this policy can be measured by (1) the number of licenses (and dollar value of affected goods and technology) pending but held up in the inter-agency process and (2) the number of licenses (and dollar value of affected goods and technology) which had been applied for by U.S. companies but not processed towards the end of the Trump Administration. (As things stood at the time of the November 3rd election, the expectation was that products in both categories which had clear 5G application would likely be rejected while non-5G products would likely be processed on case-by-case basis.)
Meanwhile, in the international sphere, the Trump Administration pursued a parallel campaign to try to persuade traditional allies to disallow Huawei technology from 5G infrastructural build-out in their respective markets on the grounds that – despite price and performance competitiveness — Huawei’s products represent a national security threat. The results of this international campaign were mixed at best, not least because many of these traditional allies had themselves been targets of different tariff sanctions under Trump’s America First trade policy. Without delving into the changing fortunes of this campaign at different times in different parts of the world, a summary headline on November 3rd might have read “Trump’s 5G Campaign Against Huawei: Embraced in India, Accommodated in the UK, Begrudged in Germany and Repudiated in Thailand and Elsewhere.”
The Biden Administration, while making a quick and clean break from Trump Administration trade policy in the area of climate change mitigation and clean energy technology, has largely kept the Trump Administration domestic policy of restrictive licensing for sales of advanced ICT goods in place. At least, it has made clear that no substantive change should be expected until after the completion of a whole-of-government review of China trade policy and a parallel review of strategic global supply chains which includes semiconductors. In the international arena, it has relaxed the narrowly-focused pressure campaign against Huawei adoption in favor of a more broadly-conceived alliance strategy to rally traditional allies and other democracies to rise to the 21st century challenge posed by China’s autocratic model.
So where do things stand today? The restriction of supplies of U.S. advanced semiconductors to Huawei under both the Trump and Biden Administrations has taken the biggest toll on Huawei. Less impactful but still a headwind for Huawei has been the doubt sown internationally as the U.S. and China edge closer towards global confrontation and supply chain de-coupling. The result? Huawei reported last Friday its third straight quarterly decline in revenues, falling a significant 38% against 2021Q1 results.
Huawei is likely to remain at the center of a highly-fraught tug-of-war between the U.S. and China over 5G. On one side, China has ability to leverage the world’s largest installed base of advanced mobile phone users in the world. On the other, the U.S. dominates the global market for the advanced microchip designs on which advanced telecom markets depend. And the U.S. maintains close partnerships with the world’s leading microchip fabricators in Taiwan and the makers of the world’s leading fabrication equipment in the Netherlands and elsewhere.
Expect more tremors and seismic activity on this fault-line for the foreseeable future. Just last week, the PRC government issued retaliatory actions against Huawei’s main Western rivals – Sweden’s Ericsson AB and Finland’s Nokia, among others. And, as fall-out from the recent spread of the SARS-COV-2 Delta-variant in China, it was announced over the weekend that the World 5G Conference – scheduled for August 6-8 in Beijing – would be postponed indefinitely. Pressure continues to mount while chances to release that pent-up pressure close off.

On January 13th of this year, President Trump abruptly ordered the termination of the U.S.-China EcoPartnership Program. Seven days before leaving office and without notice, Trump turned the lights off on this 10-year old program, pulling the rug out from under 36 committed and on-going bi-national projects to lower carbon-emissions at global scale.
The Biden Administration is assessing its options for re-vitalizing, in some shape or form, this model of innovative and impactful public-private collaboration to put a dent in global greenhouse gas emissions. This might involve replication of the program to India. ReGen250 is already in the starting gate with a U.S. Mid-Atlantic/State of Maharashtra candidate program should that take shape, as is described on pages 8-9 of our article published last month in the peer-reviewed science journal Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy.
In the meanwhile, we are pressing forward with unofficial support from the two U.S. Government agencies which ran the EcoPartnership program for ten years — the U.S. Department of State and the U.S. Department of Energy — on a purely private and sub-national basis. Our goal in China looking forward is to explore the possibility of expanding from a regional effort (low-carbon collaboration between the U.S.-Mid-Atlantic and the Jing-Jin-Ji (京津冀) region of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province to national scale.
How will we accomplish this without the direct support of the U.S. Government? The first step was to confirm the Biden Administration’s encouragement of trade with China in support of Paris Accord goals and then to renew our region-to-region BE Better program partnership with our primary partner in China, the TEDA EcoCenter. These steps were taken last quarter.
The next steps involve exploring prospects for the resumption of the Sino-U.S. Eco Park national-level opportunity with the Green Development League as outlined at the 2020 U.S.-China EcoPartnership Summit. (As described in detail in a prior post, the Green Development League comprises the 36 top-ranked NETDZs throughout China and the GDL Secretary-General is our original EcoPartnership partner (the TEDA EcoCenter and its Director Madame Yuyan Song).
As the exclusive U.S.-based working group member for the proposed Sino-U.S. Eco Park, China Partnership would leverage expertise and input from (1) our region-to-region BE Better program partners (experts in “energy-efficient, smart and healthy built environments” for industrial park users) as well as (2) our U.S.-China BEST Cities partners (with additional constituencies of support to include the U.S.-China Business Council, the U.S. Industry Advisory Board of the U.S.-China Clean Energy Research Center for Building Energy Efficiency (CERC-BEE), the National Governors Association, and the National League of Cities) in order to identify a comprehensive range of U.S. clean energy technologies and infrastructures from across eastern, central and western regions of the United States to be incorporated into the Sino-U.S. BE Better Eco Park model.

The primary impact of this milestone — CPGP’s formally joining the Green Development League’s working group for design of a Sino-U.S. Eco Park with scalability and replicability to multiple locations throughout China — is literally “to put the U.S. on the map” alongside eight other similar International Eco Parks already functioning in China under PRC Ministry of Commerce auspices. These eight other Eco Park projects represent mostly Sino-European collaborations (e.g., Sino-German Eco Park, Sino-Swiss Zhenjiang Eco Park, Sino-Austrian Eco Park, Sino-Finland Beijing Eco Park) and, to date, none represents a Sino-U.S. collaboration. The CPGP/U.S.-China BEST Cities model was selected, following the March 27, 2018 deadline for application, due to its unique structure of open collaboration designed to introduce U.S. urban clean energy infrastructures and technologies to TEDA and the 35 other top National Economic-technological Development Zones (NETDZ) in the Green Development League.
Using comparables drawn from the realized, real-world experience of the Sino-German Eco Park in Dalian but adjusted to account for the relatively greater GDP of the U.S., a Sino-U.S. BE Better Eco Park leveraging our EcoPartnership’s platform of energy-efficient, smart, healthy built environment and clean manufacturing for industrial park application should reasonably be expected to realize within its initial 5 years:
• As many as 300 signed project agreements (with nearly 60% of those either in production or under construction during that timeframe) representing total investment of 100 billion RMB (approx. USD 15 billion at today’s exchange rate)
• As many as 90 of these projects would be expected to fall in the high-end manufacturing and new energy field with total investment of 67.5 billion RMB (approx. USD 10 billion at today’s exchange rate)
• As many as 80 of these projects would be expected to fall in the advanced services sector with total investment of 35 billion RMB (approx. USD 5 billion at today’s exchange rate)
We are now actively exploring the most practical route for realizing this goal which would involve resumption, post-Trump Administration, of our primary partnership model with (a) TEDA, (b) the 36 GDLs and (c) the 219 NETDZs. Additionally, we have recourse to a secondary partnership model focused on the Jing-Jin-Ji/Xiongan New Area mega-development project.
With respect to the 35-year macroeconomic development effort ushered in by Deng Xiaoping and the Shenzhen and Pudong macro-development projects, Xiongan has both continuities and distinctive differences. One similarity is the size envisioned for the Xiongan New Area -– roughly 50% bigger than Pudong (east of Shanghai) and slightly larger than Shenzhen (to the north of Hong Kong). While Xiongan can be thought of as culminating the coastal progression of these macro-projects–- starting in the south with Shenzhen in the 1980s and moving to the central coast with Pudong in the 1990s -– the final, northern leg of this triad was wobbly at first. President Hu Jintao and Premier Wen Jiabao initially envisioned the third macro-project leg as being Binhai to the northeast of Tianjin. Post-2012, however, plans for Binhai lost most of their momentum and it was only with President Xi Jinping’s emergence in power that priority was shifted from Binhai to Xiongan. It is more in the discontinuities between Xiongan and the earlier Shenzhen and Pudong macro-projects that Xiongan’s significance can best be understood. The first 30 years of the PRC’s post-Cultural Revolution industrial development was based on a high-carbon model. (This is frequently referred to in China by the phrase 先污染后治理 meaning “pollute first, clean up (or remediate) later”). In contrast, the Xiongan industrial model championed by Xi Jinping focuses on a different set of values for the next 30-year-or-so phase of China’s development in the 21st century: the goals of (1) promoting and putting into practice low-carbon industrialization and sustainability innovations and (2) lessening social inequality and narrowing the gap between rich and poor in shared benefits of industrialization and economic development.
The following post comes courtesy of Sinosphere, the China blog for The New York Times. Like a flower poking out of the cracked pavement of a concrete jungle, this is another hopeful sign that ‘The Greening of Asia” is starting to blossom.
Q & A with Author Mark Clifford on “The Greening of Asia”
By Ian Johnson from Sinosphere, May 5, 2015 3:21am
A technician at Yingli Solar checks a solar panel on a production line at the company’s headquarters in Baoding, Hebei Province. Credit Kevin Frayer/Getty Images
After 20 years in Asia as a journalist, Mark Clifford took over as executive director of the Hong Kong-based Asia Business Council in 2007. His new book, “The Greening of Asia: The Business Case for Solving Asia’s Environmental Emergency,” explores how Asian companies are making strides in providing environmental solutions. China is a special focus because of the country’s huge emissions of carbon, but also because of its potential for innovation.
Mark Clifford.Credit Courtesy of Mark Clifford
In an interview, Mr. Clifford discussed the need to link businesses, governments and nongovernmental organizations to fight climate change:
Q.: How did you get interested in this topic?
A: I joined the Council in 2007 and inherited an almost-finished study on green buildings. That was pretty exotic in Asia back then, and we published a book on it. It got me thinking about the topic.
Q: Your angle is a bit more hopeful than some. Tell us how that came to be.
A: Originally, I thought I’d do a book along the lines of “The East Is Black.” And we do have an emergency here. In China, 1.2 million a year are dying prematurely. People need to know how bad it is, but then I got to thinking that this was pretty obvious. Instead, I thought that there are these much more positive responses underway, and people should know about them. The business community, which takes challenges and solves problems, was involved. So it is unabashedly a glass-half-full book, but that’s because it’s important to know there’s a way out. We can despair, we can do nothing, or we can work to solve one of the greatest challenges of our time.
Q; Do you see business being the main player in solving the issue?
A: No, it’s part of the solution. There has to be a three-legged stool of government, civil society and business, and each has to bring its strengths to the table. Only governments have the power to set rules — the laws and regulations, of course, but also the prices in the forms of taxes and subsidies as well as facilitating infrastructure developments. Media and NGOs make sure that business and government are doing what they promise.
Q: What was most surprising is how many companies are doing this in one form or another.
A: Yes, in the book I profile more than a dozen companies at length but also have an appendix of more than 50 companies that are involved with a variety of environmental initiatives. It was surprising to me what’s going on at the corporate level, but they’re doing things for good business reasons. Some are for the P.R. effect, but most look at it as necessary for survival.
Q: You focused one chapter on Hong Kong’s CLP Holdings, the electric power company.
A: Their work really sparked this project. In 2007, the then-chief executive, Andrew Brandler, announced that by mid-century, they would cut the carbon intensity of their electricity production by 75 percent. This pledge by one of Asia’s biggest private utilities — mostly coal-fired power plants — to effectively decarbonize by mid-century is unparalleled globally. I think this stems from the Kadoorie family, which owns a major stake in CLP. Michael Kadoorie challenges his top management to look at 50-year horizons. They do this for good reasons. They’re traditionally a coal-burning utility, but they think that this isn’t a good business model in 50 years.
Other companies think that water is underpriced, and in the future, it will be more realistically priced. Carbon also is underpriced, and other companies want to be ready for when it’s changed. But not all companies have long-term visions.To reach them, you need the other two legs of the stool. You need good, strong government policy, and you need NGOs to hold people accountable.
Q: What countries have had good policies?
A: Singapore has done an exemplary job. They decided very early on that water is of existential threat to the nation. So they have taken very firm policies, and it gives companies a form of certainty about costs.Not every country has the capacity that Singapore’s administration has, and it’s a small place with a forward-thinking government. It’s much harder in big countries like China and India, which are more fragmented.
Q: You have a lot on China.
A: The good news is we have good policies coming down from the top levels of the Chinese government. Where China continues to struggle is the implementation at the ground level. There’s not always enforcement, and there’s no civil society to act as a check. The time when China decides that the environment and energy issues are as much of a threat as the color revolutions were, or the Hong Kong protests were last year, that’s when we’ll know we have serious progress. We’ve seen with Chai Jing [whose popular documentary film on the environment, “Under the Dome,” was banned] that civil society is muted.
Q: We read a lot about air pollution, but you also think that water is crucial.
A: Increasingly, water is a hard-stop issue. Air pollution is horrible, but most people affected by it are still living. But no one can live without water. I don’t know what people will do when the water stops. In China, projects like the South-North Water Diversion Project just delay the day of reckoning. What concerns me is that even most otherwise far-sighted governments are not facing up to the challenges. For example, what do you do if you’re a municipal official, and you have an industry, say semi-conductors, which uses a lot of water? What do you do when you have to make a choice: water for the factory or the town? These are the kinds of choices that aren’t going to happen today or tomorrow, but governments will face this.
Q: And yet there are signs of hope in China.
A: China is about to overtake Germany as having the largest amount of installed solar power capability. It also has large wind turbine facilities. All of this is important because China burns half the world’s coal and accounts for 30 percent of carbon dioxide emissions. So to fix China, we need to cut coal use. Coal is supposed to peak in 2030, but it could happen a lot faster. So these are huge challenges, but China is potentially further ahead than many people realize.
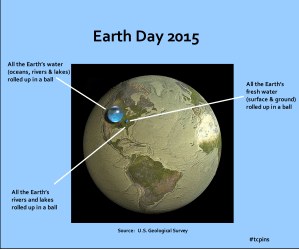
Hard to believe? Here’s the data behind it. Three cheers for water!